Supply Chain Security: A Comprehensive Overview

Supply chain security is important to protect the integrity and confidentiality; availability of information and services. By addressing both physical and cyber threats, we can mitigate risks and ensure a resilient supply chain. Let us understand the importance, common threats, challenges, and future trends of supply chain security for maintaining an efficient and secure supply chain.
Supply Chain Security: An Overview
Supply chain security involves the measures taken to protect the entire supply chain ecosystem from potential risks that could compromise data, disrupt operations, cause financial losses, and damage reputations. It involves both physical security (protection of goods in transit) and cybersecurity (protection of digital information).
The year 2024 witnessed around 183,000 customers globally affected by supply chain cyberattacks, a significant drop from over 263 million in 2019. However, in the first quarter of 2023 alone, over 60,000 customers reported being affected by such attacks. Common cyber threats included forging, drive-by compromise, and malware infections - Statista reports
The World Economic Forum's ‘Global Risks Report 2024’ highlights cybersecurity as a constant concern, predicting continued risks from technology-enabled resources and services in the year 2025. Also, Gartner forecasts that by 2025, 45% of global organizations will be affected in some way by a supply chain attack.
A Brief History of Supply Chain Attacks:
By understanding the history and evolution of supply chain attacks, businesses can better prepare and implement measures to protect against such threats. Here's a brief history of few top-notch incidents:
Early Examples of supply chain attacks
- 1982: Agent Farewell and the Siberian Pipeline Explosion: In this case, the U.S. exploited the Soviet Union's efforts to acquire Western technology by deliberately providing them with faulty software. This software, once integrated into the Soviet supply chain for controlling the gas pipeline, prompted a catastrophic failure.
- 2003: Cisco Router Attack: It is concerned with the tampering of Cisco routers during manufacturing. Attackers installed malicious firmware to gain unauthorized access to networks through these routers.
Major Incidents
- 2013: Target Breach: The attackers compromised the retailer's HVAC vendor, Fazio Mechanical Services. Using stolen credentials, they installed malware on Target's point-of-sale systems, resulting in the theft of 40 million credit and debit card details.
- 2017: Not Petya Attack: This attack targeted the Ukrainian financial software company- Medoc. Hackers inserted malware into a software update, that spread globally, affecting companies like Maersk and Merck. The attack caused an estimated $10 billion in damages.
Most recent supply chain attacks
- 2018: Operation Shadow Hammer: Attackers compromised the update mechanism of ASUS's Live Update utility, distributing malware to over a million users. This sophisticated attack highlighted the risks associated with software supply chain.
- 2020: SolarWinds Attack: It is one of the most significant supply chain attacks in recent history. It involved the insertion of malicious code into the Orion software platform, allowing attackers to access the networks of several government agencies and private companies.
Let us discover the impact and intensity of supply chain attacks by revisiting the cyberattacks occurred in the last two years. Take a look at top supply chain cyberattacks in last 2 years.
Top Supply Chain Cyberattacks in 2024
| Months | Attack | Nature of Attack | Loss Incurred | Action Taken |
| December | Salt Typhoon and Volt Typhoon | Targeted U.S. telecom providers and critical infrastructure | Significant reputational damage occurred | Mitigated the impact and improved security services |
| November | Blue Yonder supply chain attack | Ransomware attack by Shadowcrew targeting blue yonder’s supply chain management software | Targeted food and retail companies -Starbucks, Morrisons, Tesco, Sainsbury’s, etc. | Engaged external cybersecurity firm, contained breach, and prevented further unauthorized access |
| October | Casio phishing-based Ransomware attack | Penetrated Casio’s IT infrastructure leading to IT outages and data breach | Breach affected 8500 individuals | Engaged external cybersecurity firm, contained breach, improved security systems, did not pay any ransom demand |
| September | Internet Archive Attack | Attackers exposed sensitive data | Significant reputational damage occurred | Secured the systems |
| August | OpenSSH "regreSSHion" Vulnerability | Attackers bypassed authentication | No financial loss reported | Released patches and fixed the vulnerability |
| July | Fortinet Vulnerabilities | Multiple vulnerabilities existed | No financial loss reported | Released patches and updated systems |
| June | Cisco Duo Supply Chain Data Breach | Compromised sensitive information | Reputational damage | Enhanced security measures |
| May | Cooler Master | Attackers exfiltrated 103 gigabytes of data | The breach affected over 500000 individuals | Offered support services, and notified relevant law enforcement agencies |
| April | SiSense Attack CrowdStrike Linux Outage | Attackers gained access to SiSense’s GitLab code repository Attackers used token to access company’s Amazon S3 buckets and obtained several terabytes of customer data A] Faulty software update B] Kernel bug in Debian and Rocky Linux | Millions of access tokens and email account passwords compromised A] Estimated $5.4 billion loss B] Caused significant operational disruptions | Customers were asked to reset credentials. The breach did not interrupt business operations A] Developed and deployed restore tool B] Rigorous testing |
| March | XZ Utils Backdoor Attack | Attackers embedded malicious code into the XZ Utils compression utility | No significant financial loss reported | The backdoor was discovered and removed before it could cause any major damage |
| February | Change Healthcare Ransomware Attack | Alphv/BlackCat ransomware group disrupted healthcare services nationwide and exposed >100 million individuals' sensitive medical data. | Estimated $46,000 in ransom payments | Restored services and enhanced security measures |
| January | Midnight Blizzard | A sophisticated attack targeted Microsoft executive | Significant reputational damage occurred | Improved security protocols |
Top Supply Chain Cyberattacks in 2023
| Months | Attack | Nature of the Attack | Loss Incurred | Actions Taken |
| December | Public services as C2 (command and control) infrastructure | Malware authors hosted second stage malware to fetch real C2 server address by using platforms like GitHub, Google Drive,etc. | Data theft and operational disruption | Users and organizations were notified, and security measures were enhanced. |
| November | Protestware software | -Developers modify their own code or software libraries to protest events/policies. - Political messages were added in repository files, altering package descriptions, or breaking the software functionality | Operational distribution Loss of trust | - Cybersecurity researchers removed the protest ware. - There were community discussions about the ethics and consequences of protestware |
| October | IAmReboot | The attackers exploited the loophole in the MSBuild integrations, mimicked NuGet packages prompting users to download | Data theft and operational disruption | Detection and removal of malicious packages, users were notified, and security measures were enhanced |
| September | JetBrains Supply Chain Attack (Sep/Oct 2023) | Exploitation of CVE-2023-42793 in TeamCity CI/CD software | Compromise of source code, signing certificates, and software compilation processes | Patches released, security updates applied, threat hunting initiated |
| August | VM Connect attack | The malicious packages name created resembled with legitimate ones like eth-tester, V Connector, prompting users to download | Identity theft and operational disruption | Malicious packages were removed from PyPI, and users were notified. |
| July | Microsoft365 Forged Access Token | Forged authentication tokens used to access email accounts | Unauthorized access to email accounts of ~ 25 organizations | Mitigations implemented, malicious tokens blocked, customers notified |
| June | JumpCloud | -Spear-phishing campaign targeted a JumpCloud software engineers, tricked them to download malicious code. -The attackers gained developer-level access and launched workloads in the container orchestration system. | A few JumpCloud customers and devices were impacted. | Revoked system access, notified impacted customers, improved security measures. |
| May | MOVEit | Zero-day vulnerability: The attackers exploited the flaw in the SQL injection, gain unauthorized access to MOVEit servers, and deploy malicious scripts. | - Estimated $9.93 billion loss - 2000 organizations were influenced - Impacted 60000 individuals | - Contained the breach through a patch - Affected organizations were notified - Improved security measures |
| April | NCB Managed Services, US based debt-collector | Attackers gained unauthorized access to sensitive financial information | Data breach affected 494,969 individuals | - offered two years of free identity theft protection services for affected individuals -paid ransome amount |
| March | Imposter HTTP Libraries | 41 malicious packages on Python Package Index (PyPI) posed as HTTP libraries | Data theft that will lead to further cyberattacks | -The PyPI package was removed from the repository |
| February | Aabquerys | Aabquery package mimicked the Node Package Manager, prompting developers to download | Data theft that will lead to further cyberattacks | -The NPM package was removed from the repository |
| January | Slack GitHub Repositories Visual Studio Code extensions in the marketplace | Theft of employee tokens used to access GitHub repositories Multiple extensions were linked to same author, and engineered to steal data | Downloaded Private code repositories VS Code extensions got downloaded 46,600 times | -Tokens invalidated, credentials rotated, increased monitoring implemented -VS Code extensions were removed from the marketplace. Microsoft and Cybersecurity firms improved security measures. |
To sum up, supply chain attack has become more prevalent and impactful. High-profile incidents like the SolarWinds and the JetBrains supply chain attack serve as wake-up calls instigating the need for robust security measures.
Moving forward, let’s explore how organizations are exposed to the risks of supply chain cyberattacks and their implications.
Common Risks in Supply Chain Security
Supply chain attacks expose organizations to various risks. It creates a negative impact on integrity and operations. A few of them are highlighted here.

Figure 1: Risks in Supply Chain Security
Types of Supply Chain Cyberattacks
The attackers target different vulnerabilities within the supply chain. Accordingly, the most common types of attack are:
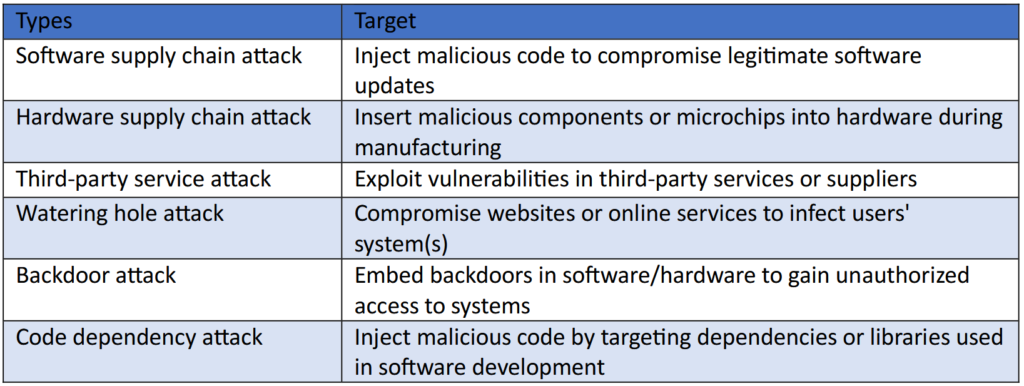
Importance of Supply Chain Security
At this point, it is clear that Supply chain attacks pose real and significant threats to businesses and consumers alike. The key lies in having a secure supply chain. It helps protect sensitive information, prevents disruptions, and maintains customer trust. In addition, it can reduce the risk of financial losses and legal liabilities.
Addressing the supply chain attack risks requires a multi-layered approach.
Let’s restate some of the key initiatives to improve supply chain security. It includes
- Managing access
- Designing and monitoring supply chain
- Developing a robust response plan
- Securing log collection and management
- Utilizing technology for real-time visibility
- Enhancing cyber supply chain risk management
- Integrating suppliers into resilience and improvement initiatives
- Identifying vulnerabilities
- Ensuring compliance with regulatory standards
- Collaborating with industry partners
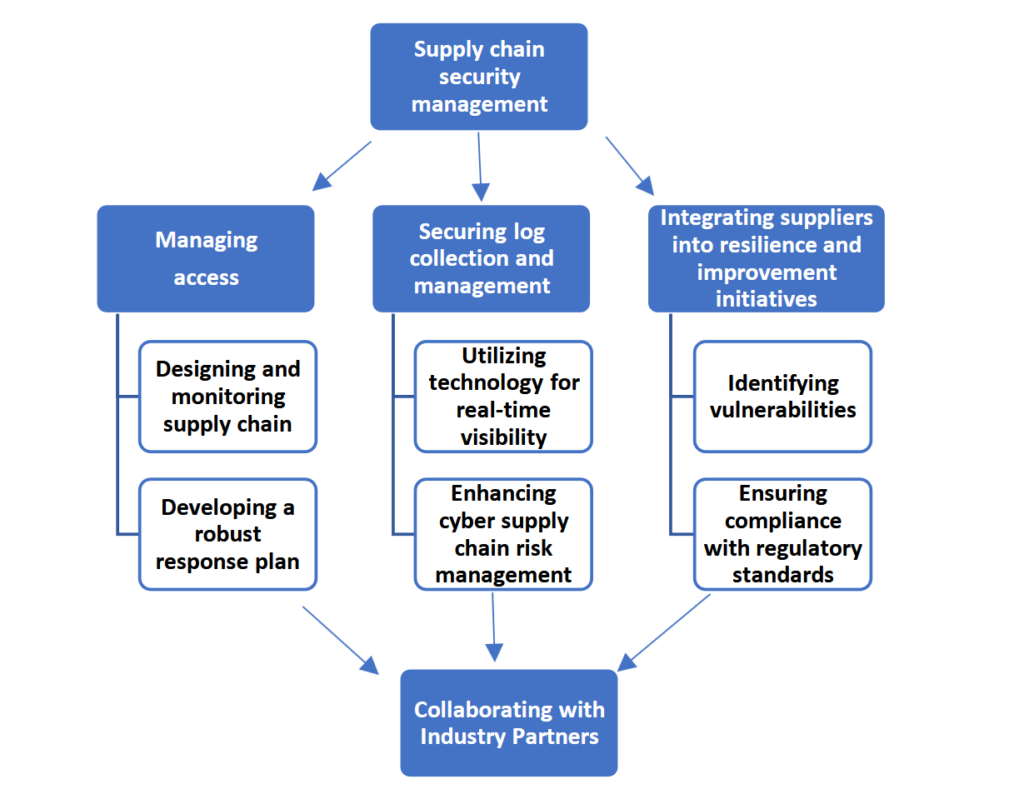
Figure 2: Key Initiatives to Improve Supply Chain Security
Conclusion:
Effective supply chain security requires collaboration among businesses, customers, and IT organizations. By implementing robust security measures, organizations can mitigate risks and ensure the secure and efficient movement of products and services.
As mentioned earlier, collaborating with governments, cybersecurity firms, and organizations enable organizations to follow best practices. Focusing on resilient supply chains help to recover from disruptions quickly.
As the threats continues to evolve, staying informed about future trends and advancements in technology is essential for maintaining a secure and efficient supply chain. Leveraging blockchain technology, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning will help in automated monitoring and tamper-proof tracking of transactions.
Looking to Strengthen Your Supply Chain Security?
Finding the right partner is the key. At AuthenticOne, our managed security services empower organizations to understand and address emerging threats proactively.
Reach out to us today for a complete assessment of your supply chain security needs and gain custom-made solutions.
Advisory & Compliance Services
Audit & Assessment Services
Managed Security Services
Governance & Compliance Framework Development
Cyber Key Performance IndicatorsCISO Advisory
Advisory and Compliance ServicesStandard & Regulatory AdvisoryBusiness Continuity & Disaster Recovery PlanningIncident Response ReadinessData Privacy
Audit and Assessment Services
Cloud Security Assessment
Cyber Maturity Assessment
Privacy Impact Assessment
Red Teaming Service
VAPT
Managed Security Services
SOC as a Service
Third Party Risk Management
Vulnerability Management Services